Information and Communication Technology
As ICT is becoming more and more part and parcel of teaching, it would be interesting to see how ICT has developed through the last decades.
This article aims at helping teachers have a general idea of the history of ICT, from the invention of the first computer up to now. We will also try to peep into the future to see how ICT will look like in the next few decades.
A brief history of ICT
The telegraph (1837) and telephone (1876) permitted communication by wire over long distances almost instantaneously, a vast improvement over the earlier methods of rail, ship and pony express. Communication by wireless telegraph (1895), shortwave radio (1926) and then more reliable high-frequency microwave radio (1946) overcame the physical constraint of connecting every point by wire or cable. Microwave provided larger-capacity communication channels for transmitting television signals and set the stage for the development of satellites and space communication (1957). In the 1970s, mobile communication handsets were developed, as was the basic technology foundation for the Internet and the World Wide Web. Both mobile and Internet communication have grown rapidly since their introduction in the 1980s to the point where mobile access to the Internet (e.g., smartphones) is the dominant and fastest growing form of communication.
The primary thrust of information and communications technology (ICT) development in the 21st century is to expand both the capabilities and the capacity of the equipment and facilities used to communicate over telecommunication networks. Through the 1990s and 2000s, the term technological convergence became the catchphrase to describe the way new ICT are being used to bring together what were previously separate communication media — like voice telephone, radio, TV, newspapers and computer data — into one medium, the Internet, provided over enhanced, high capacity broadband telecommunication networks.
As ICT have continued to improve and the Internet has expanded to near universal coverage in most developed countries, software-based network applications are being developed and applied far beyond the information and communication industries: in the banking, retail and services sector; in industrial production, agriculture, education and medical services; and in government services ranging from issuing licenses to taxation. Increased capabilities for gathering enormous volumes of detailed information (meta data) and the establishment of networks of communicating devices (e.g., Internet) have provided new opportunities for beneficial applications in fields such as science, health and environmental monitoring, but also facilitated serious erosions of privacy by enabling spying on individuals and organisations by governments, corporations and sophisticated hackers.
HISTORY OF INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY
- The prehistoric period
a. Period (…. S / d 3000 BC)
At first humans developed information technology at this time serves as a system for the introduction of the forms that they know. They describe the information they get on the walls of the cave, about hunting and prey animals. At this time they began to identify objects that exist in the environment they live and represent it with the forms which they then painted on cave walls tempa.t they live, because of their ability to speak only about the form of voice grunts and hand gestures as a form of their initial communication at this time. Further development is created and use the tools that generate sounds and cues, such as drums, trumpets made of animal horn, or smoke signals as a means of giving warning of danger.
b. Period of 3000 BC For the first time used by the Sumerians writing with symbols formed from pictograf as letters. Symbols or letters also have a different sound form (mention), so it can be words, sentences and language.
c. Historical Period (3000 BC s / d in 1400-an M)
1) 2900 BC
The use of letters hierogliph on the ancient Egyptians. Hierogliph a language of symbols where each phrase is represented by different symbols. When combined into one will have a way of pronunciation and different meanings. Heirogliph form of writing and language is more advanced than Sumerian writing.
2) 500 BC
Papyrus fibers are used as paper. Paper made from papyrus tree fiber that grows around the Nile is a medium for writing or media information that is more powerful and flexible than the clay tablets that were previously used as a medium of information.
3) 105 M
The Chinese discovered kertas.Kertas discovered by the Chinese at this time is the paper that you know today. Paper is made from bamboo fibers are crushed, filtered, washed, then flattened and dried. The invention also allows the printing system is performed using a carving on a block of wood and covered by the ink or what we know today with a cap.
2. MODERN PERIOD (1400-S AN M / D NOW)
a. Year 1455
The printing press that uses the letters are made of iron plate that can be changed in a frame made of wood was developed for the first time by Johann Guntenberg.
b. Of 1830
Augusta Lady Byron wrote the first computer program in the world to work with Charles Babbage’s Analytical engine it uses. The tool is designed to be able to enter data, process data, and generate output in the form of a card. This machine is known as a form of the first digital computer, although the way it works is more mechanical than is digital, 94 years before the first digital computer ENIAC 1 is formed.
c. In 1837
Samuel Morse developed the telegraph and Morse code language with Sir Wiliam Cook and Sir Charles Wheatstone who sent electronically between two distant parties through the cable connecting the two places. Sending and receiving of this information can be sent and received at almost the same time this invention allows the information can be accepted and used widely by the people unhampered by distance and time.
d. In 1861
Moving images are projected onto a screen was first used as the precursor film is now in ancient times as the projector is growing step on the screen. e. During the year 1876 was marked by figures who developed the Melvyl Dewey decimal system of writing.
f. In 1877
1) Alexander Graham Bell invented and developed the first time used the phone in general.
2) high-speed photography was invented by Edward Maybridge.
g. In 1899
Used in tape storage system (tape) the first magnetic storage but at this time is still analog not digital like the present. h. During the year 1923 was marked by Zvorkyn creating the first television tubes.
i. In 1940
Commencement of the development of science in the field of information during World War 2, which is used for the benefit of sending and receiving of military documents that are stored in the form of magnetic tape.
j. In 1945 Vannevar Bush developed a coding system using hypertext.Pada this period the use of hypertext has been developed along with the development of website design is currently evolving.
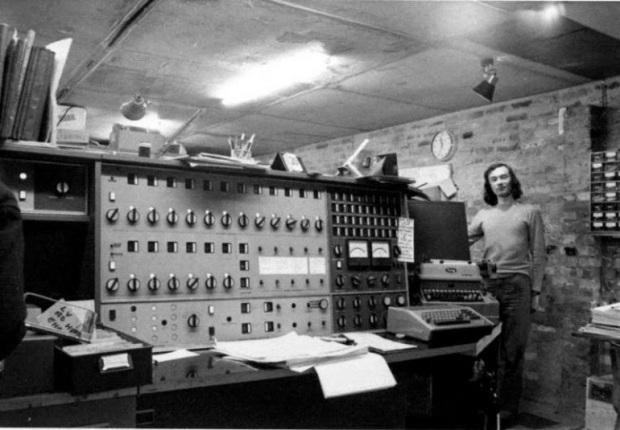
k. During the 1946 period of this technology in the world’s first digital computer ENIAC was developed although I have not so many users, but computer technology has been used certain agencies.
l. Year 1948
Researchers at Bell Telephone developed the transistor.
m. Year 1957
1) Jean Hoerni developed the planar transistor. This technology allows the development of millions and even billions of transistors incorporated into a small piece of silicon crystal.
2) USSR (Russia at the time) as the launching of Sputnik the first artificial earth satellite who served as a spy. In return the U.S. to form the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) under the authority of the Department of Defense to develop science and information technology in the military field.
n. Year 1972
At this time Ray Tomlinson created the first e-mail program that is used to communicate over long distances using teks.E-mail can be said as electronic mail.
o. Year 1973-1990
The term Internet was introduced in a paper on TCP / IP and then made the development of a network protocol known as TCP / IP was developed by a group of DARPA.Pada the 1981 National Science Foundation to develop a backbone called CSNET 56 Kbps capacity for each institution in pemerintahan.Kemudian in 1986, the IETF developed a server that serves as a coordination tool including: DARPA, ARPANET, DDN, and Internet Gateway.
p. Year 1991 –
Now the business systems in the IT field first occurs when the CERN in overcoming operational costs a fee from its members. In 1992 the establishment of the Internet community, and then introduced the term World Wide Web (WWW) by CERN.Pada 1993, NSF established the InterNIC to provide Internet related services and data storage directories and databases (by AT & T), registration services (by Network Solutions Inc. ), and information services (by General Atomics / CERFNET). In 1994 the growth of the Internet drove very fast and began reaching into all aspects of human life and a part that can not be separated from manusia.Tahun 1995, public enterprises began to be allowed into the provider by purchasing network in this Backbone.Langkah began development of information technology especially the internet and research to develop systems and more sophisticated tools.
Computers
The term “computer” comes from the Latin “computus” and “computare”. Both Latin words mean to determine by mathematical means or by numerical methods. The English verb “compute” has the same meaning.
Basically, a computer is a programmable electronic device that performs mathematical calculations and logical operations, especially one that can process, store and retrieve large amounts of information very quickly. Personal computers are also employed for manipulating text or graphics, accessing the Internet, or playing games or media.
The main components of a computer are:
- a Central Processing Unit (CPU),
- a monitor,
- a Keyboard,
- and a mouse.
Originally the first computers were the size of a large room, consuming as much power as several hundred modern personal computers.

The US-built ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) was the first electronic programmable computer built in the US.
Later, computers have become smaller and much more powerful.
The Internet
The Internet was invented as a result of researches conducted in the early 1960s by visionary people like J.C.R. Licklider of MIT. The latter saw the added value of allowing computers to share information on research and development in scientific and military fields. That’s why, he proposed a global network of computers in 1962, and moved over to the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) in late 1962 to head the work to develop it.
The Web
While many people use the terms Internet and the Web interchangeably, they are in fact not synonymous. The Internet is a huge network that connects millions of computers together worldwide. Computers in this network can communicate with any other computer as long as they are connected to the Internet. The Web or theWorld Wide Web (WWW), however, is a way of accessing information over the medium of the Internet. It is an information space or a model that is built on top of the Internet where documents and other web resources are identified by URLs (Uniform Resource Locator), informally termed a web address. This space is interlinked by hypertext links, and can be accessed via the Internet.
The World Wide Web was invented by English scientist Tim Berners-Lee in 1989. He wrote the first web browser in 1990 while employed at CERN in Switzerland.
Web 1.0, Web 2.0, and Web 3.0
What’s the difference between Web 1.0, Web 2.0, and Web 3.0?
They represent the evolution of the Web in the last two decades. Here is a summary of their features.
Web 1.0
Web 1.0 was the first stage of the World Wide Web’s evolution. Basically, content creators provided content for the vast majority of users who were only consumers or readers of that content.
The most important features of Web 1.0 were as follows:
- It was a read only web
- It was based on HTML which is a basic computer language.
- It was characterized by static pages (there is no interactivity between users and websites).
- It was also characterized by slow connection speed.
- The software was very expensive, generally on CDs or DVDs to be installed.
Web 2.0
Web 2.0 was the next evolution of the Web. It is more sophisticated and is characterized by its social aspect. Unlike Web 1.0, Web 2.0 is a many-to-many relationship.
Here are the features of Web 2.0:
- It is a read-and-write web.
- It is based on more sophisticated computer languages (PHP, Mysql, Java Script…)
- The pages are dynamic pages, which means that there is the possibility of interactivity between users and the web.
- It is characterized by speed.
- The software is more accessible. It is on line or downloadable.
Web 3.0
Web 3.0 is an evolution of the Web as an extension of Web 2.0. It is also called the Semantic Web. It is characterized by connective intelligence, connecting data, concepts, applications and ultimately people.
Here are its features:
- Read, write and execute web.
- Users are served more intelligently.
- Personalized information.
- Machine comprehension.
- Cloud Technology.
- Everything is connected.
- Immersion.
ICT for education
Many educators saw in ICT the potential of raising the quality of teaching and learning. Here is what it can offer to education:
- Universal access to high quality education.
- Teachers’ professional development.
- Efficient education management in terms of governance and administration.
- Promotion of equity in education.
For teachers, ICT offers a mine of content, material, and ideas.
Examples of ICT tools
ICT can offer different Web tools:
- websites
- wikis
- blogs
- forums
- applications
- …
And the list is not exhaustive.
What’s next?
The future of ICT is promising. The web will develop even more possibilities.
Web 4.0
Web 4. or the symbiotic web will lead to an interaction between humans and machines in symbiosis. Machines would be clever on reading the contents of the web and react fast by providing superior quality content.
Web 5.0:
Web 5.0 or the emotional web is a version that is still developed underground. The web will interact with users and will be able to recognize their emotions. So far the web is neutral as far as emotions are concerned. This will probably change in the future.
INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY AND EDUCATION
A Changed World With Unchanged Classrooms:
If you compared our world today with the world one hundred years ago , you would encounter amazing advances in science , commerce , health care , transportation and countless other factors . But if you were to compare the classroom of a hundred years ago with an average classroom today , you would recognise it immediately : students lined up in rows , paper & pencil in hand ; a teacher at the blackboard jotting down important facts ; students furiously copying all that is written & said , expecting to memorise the facts & spit them out on an exam .
-HARVARD UNIVERSITY REPORT , 2002
ADVANTAGES OF ICT:
- Increasing access through distant learning.
- Enabling a knowledge network for students.
- Training teachers.
- Broadening the availability of quality education materials.
- Enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of educational administration and policy.
- Social skills.
- Research and development.
- Professional development.
- Policy and strategic planning.
Information and Communication Technology (ICT) can contribute to universal access to education, equity in education, the delivery of quality learning and teaching, teachers’ professional development and more efficient education management, governance and administration.ICTs stand for information and communication technologies and are defined, for the purposes of this primer, as a “diverse set of technological tools and resources used to communicate, and to create, disseminate, store, and manage information.” These technologies include computers, the Internet, broadcasting technologies (radio and television), and telephony.
In recent years there has been a groundswell of interest in how computers and the Internet can best be harnessed to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of education at all levels and in both formal and non-formal settings. But ICTs are more than just these technologies; older technologies such as the telephone, radio and television, although now given less attention, have a longer and richer history as instructional tools. For instance, radio and television have for over forty years been used for open and distance learning, although print remains the cheapest,most accessible and therefore most dominant delivery mechanism in both developed and developing countries. The use of computers and the Internet is still in its infancy in developing countries, if these are used at all, due to limited infrastructure and the attendant high costs of access.
Moreover, different technologies are typically used in combination rather than as the sole delivery mechanism. For instance, the Kothmale Community Radio Internet uses both radio broadcasts and computer and Internet technologies to facilitate the sharing of information and provide educational opportunities in a rural community in Sri Lanka. Similarly, the Indira Gandhi National Open University in India combines the use of print, recorded audio and video, broadcast radio and television, and audio conferencing technologies.
What is e-learning?
Although most commonly associated with higher education and corporate training, e-learning encompasses learning at all levels, both formal and non-formal, that uses an information network—the Internet, an intranet (LAN) or extranet (WAN)—whether wholly or in part, for course delivery, interaction, evaluation and/or facilitation. Others prefer the term online learning. Web-based learning is a subset of e-learning and refers to learning using an Internet mainly using a browser (such as Chrome or Firefox or Internet Explorer).It can also be viewed as learning through the use of electronic devices.
Technology and ICT have been drivers that have re-engineered our society and commerce in recent years. Some might say they have presented opportunities for change that have lead to unique benefits. Just as in any market, we have seen both pioneers and early adopters and, at the opposite end of the spectrum those schools that are slow and reluctant to accept change . ICT is a network which connect people worldwide.
Across England, Wales and Northern Ireland, the ICT Mark, administered by Naace, is a good indicator of the maturity achieved by schools in their use of ICT in Leadership and Management, Planning, Learning, Assessment, Professional Development and use of Resources. Over 2000 schools have achieved this quality mark and can demonstrate their effectiveness in their use of ICT delivering benefits to all aspects of school and student life and extending more broadly into the community.
No one can deny the impact that technology continues to have on almost every aspect of our daily lives, nor the speed with which new developments are adopted by us. The mobile phone is ubiquitous, and not just for anytime anywhere voice communication. Broadband data connectivity brings access to the Internet and our personal and business communications. GPS can give us geographical guidance. A camera gives us video as well as image and sound recording capability, and local storage continues to get ever larger and ever cheaper.

With the introduction of “apps” we now have almost untold free or low cost support to use and manage the information to which we have access. With the developments in “Cloud” computing, and the expansion of the Internet to “connected things” as well as people our access to, and use of information continues to evolve relentlessly.Today it is the norm to use a range of personal data tools that specifically suit our needs. Tablet computers such as the iPad are popular for publications such as newspapers or books and magazines, delivered digitally. Along with laptops and MP3 players they offer us portability – anytime anywhere access.
The past decade has seen the rapid development of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) in many areas of the global economy. The impact of changes could be varied depending on a number of factors and it could be hard to mention all relevant stuff within the limit of this post. Therefore, the music industry, one of the industries in which the changes could be obviously recognized, will be taken to be the focus of the analysis. The purpose of this paper is to review the development of ICT during the period of 2001 – 2009 and its impact on the growth of the music industry.Based on the purpose above, the paper has been divided into three main parts. The first part deals with how the ICT affected the interactions with customers and suppliers. It will then go on to the impact of ICT on the marketing aspect of the industry. Finally, there will be some conclusions as well as the development forecast for the coming years.